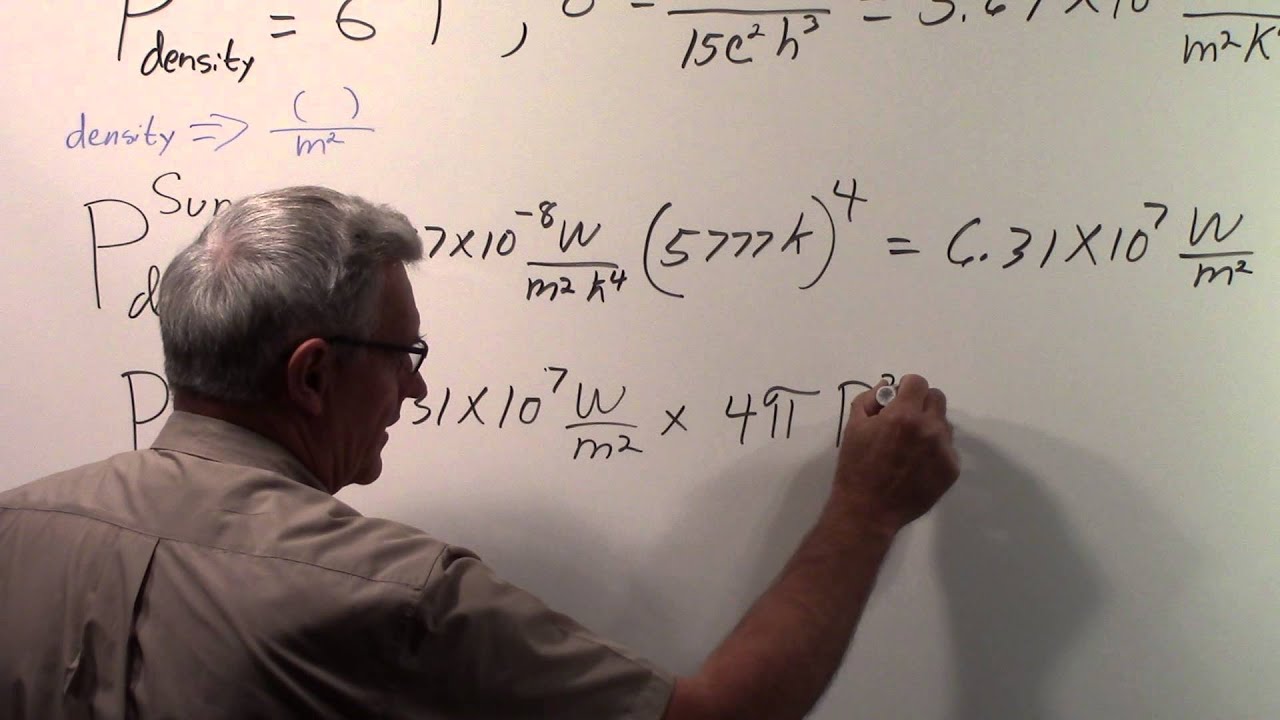The solar constant is the amount of solar radiation that a planet receives from the sun. It is a measure of the amount of power that the sun delivers to a planet. The solar constant is usually measured in watts per square meter (W/m2).
It is a important factor in determining the climate of a planet. The solar constant can be calculated using the following formula: solar constant = solar flux / distance2.
- Find the planet’s average distance from the sun
- Find the planet’s average orbital speed
- Find the planet’s solar irradiance
- Use the inverse-square law to calculate the solar constant

Credit: study.com
How Do You Find the Solar Constant on Venus?
Assuming you would like tips on finding the solar constant on Venus:
The solar constant is the amount of power that the sun emits per unit area. It is usually measured in watts per square meter (W/m^2).
There are a few ways to find the solar constant on Venus. One way is to use a pyranometer. A pyranometer is a device that measures the amount of sunlight that hits a given area.
By pointing the pyranometer at the sun and measuring the amount of sunlight that is received, you can calculate the solar constant.
Another way to find the solar constant is to use a solar flux sensor. A solar flux sensor measures the amount of sunlight that is emitted by the sun.
By pointing the sensor at the sun and measuring the amount of sunlight that is received, you can calculate the solar constant.
The solar constant can also be calculated by using the Stefan-Boltzmann law. The Stefan-Boltzmann law states that the power emitted by a black body is proportional to the fourth power of its temperature.
The sun is a black body, and its temperature can be measured by using a spectrometer. By measuring the temperature of the sun and plugging it into the Stefan-Boltzmann law, you can calculate the solar constant.
Once you have measured or calculated the solar constant, you can then use it to calculate the amount of power that the sun emits.
The sun emits a lot of power, and it is important to be able to accurately measure it. By knowing the solar constant, you can better understand the power of the sun and how it affects the planets.
What is the Solar Constant Value?
The solar constant is the amount of power that the Sun emits in the form of electromagnetic radiation per unit of area. It is measured in watts per square meter (W/m2). The value of the solar constant is about 1366 W/m2.
This value is not actually constant, but it varies by about 1.3% over the course of a year. The reasons for this variation are not fully understood, but it is thought to be due to changes in the Sun’s magnetic field.
How Do You Find the Solar Constant on Mars?
The solar constant is the average amount of solar radiation that reaches the Earth’s atmosphere. It is measured in watts per square meter (W/m2). The solar constant varies slightly over the course of the year and from one location to another.
It also varies depending on the amount of cloud cover.
To find the solar constant on Mars, you need to first find the average amount of solar radiation that reaches the planet’s atmosphere. This can be done by measuring the amount of sunlight that hits the planet’s surface.
The solar constant can then be calculated by dividing the average amount of solar radiation by the surface area of Mars.
The solar constant on Mars is about 590 W/m2. This is lower than the solar constant on Earth, which is about 1,000 W/m2.
The lower solar constant on Mars is due to the fact that the planet has a much thinner atmosphere than Earth. This means that less sunlight is able to reach the surface of Mars.
How Do You Calculate the Solar Constant of Jupiter?
Assuming you want the solar constant at Jupiter’s surface:
The solar constant, sometimes called the nominal solar constant, is the average amount of power that the Sun delivers to a unit area (usually expressed in watts per square meter) at a distance of one astronomical Unit (AU) from the Sun. Just like the brightness of a star, the solar constant is inversely proportional to the square of the distance from the Sun.
The solar constant is a measure of the average power delivered by the Sun over the entire surface of a planet.
The solar constant of Jupiter can be found using the following equation:
Solar Constant = (Luminosity of the Sun) / (4 * π * (Distance from Sun to Jupiter)2)
Where:
Luminosity of the Sun (L⊙) = 3.828×1026 W (watts)
Distance from Sun to Jupiter (AU) = 5.2
Therefore, the solar constant of Jupiter is:
Solar Constant = (3.828×1026 W) / (4 * π * (5.2)2)
Solar Constant and Solar Intensity on Earth
Solar Constant Formula
The Solar Constant, also known as the Solar Constant of the Earth or the Solar Constant of the Sun, is the amount of power that the Sun emits per unit area. It is a measure of the average amount of solar radiation that hits the Earth’s atmosphere. The Solar Constant is not a constant value, but it varies depending on the Earth’s distance from the Sun and the Sun’s position in the sky.
The Solar Constant is about 1361 watts per square meter. This value is an average over the entire surface of the Earth. The value can be higher or lower depending on the time of day and the time of year.
The Solar Constant also varies depending on the location on the Earth’s surface.
The Solar Constant is important because it is the main source of energy for life on Earth. The Sun’s energy drives the Earth’s climate and weather.
It also provides the energy for photosynthesis, which is the process that plants use to create food. The Solar Constant also affects the Earth’s oceans and atmosphere.
How to Calculate Solar Constant for Mars
If you want to calculate the solar constant for Mars, you’ll need to know the average distance from the sun, and the solar luminosity. The average distance from the sun is 1.5 AU (astronomical units). The solar luminosity is 0.0059 x 3.828 x 1026 W. With these two numbers, you can plug them into the equation: Solar Constant = Solar Luminosity / (4 x π x (Distance from Sun)2).
This will give you the solar constant for Mars, which is 1.365 kW/m2.
What is the Value of Solar Constant in W/M2
Solar constant is the measure of the solar radiation that hits the Earth’s atmosphere. It is measured in watts per square meter (W/m2). The value of the solar constant is generally taken to be 1,368 W/m2.
This value can vary slightly, depending on the time of day, the time of year, and the location on Earth. The solar constant is an important factor in determining the Earth’s climate. It affects the amount of solar radiation that reaches the surface of the Earth, and thus the amount of heat that is available to drive the Earth’s weather and climate.
Solar Constant of Earth
The solar constant is the amount of power that the sun produces per unit area that is perpendicular to the sun’s rays. It is a measure of the solar intensity at a particular distance from the sun. The solar constant is important because it determines the amount of power that is available for solar energy systems.
The solar constant is measured in watts per square meter (W/m2). The average solar constant is 1,368 W/m2. However, the solar constant varies depending on the distance from the sun and the time of day.
For example, the solar constant is highest at the equator and lowest at the poles.
The solar constant also varies over the course of a year. The sun is closer to the earth in January than it is in July.
As a result, the solar constant is higher in January than it is in July.
The solar constant is a important factor in the design of solar energy systems. Solar energy systems must be designed to collect the right amount of power to meet the needs of the system.
If the solar constant is too low, the system will not produce enough power. If the solar constant is too high, the system will produce more power than necessary and the excess power will be wasted.
Conclusion
The solar constant is the amount of power that the sun emits per unit area. It is a measure of the sun’s intensity and is used to calculate the amount of power that a planet receives from the sun. The solar constant is a function of the sun’s distance from the planet and the planet’s distance from the sun.
The solar constant is measured in watts per square meter and is a function of the sun’s distance from the planet and the planet’s distance from the sun. The solar constant for a planet is calculated by dividing the power of the sun by the surface area of the planet.