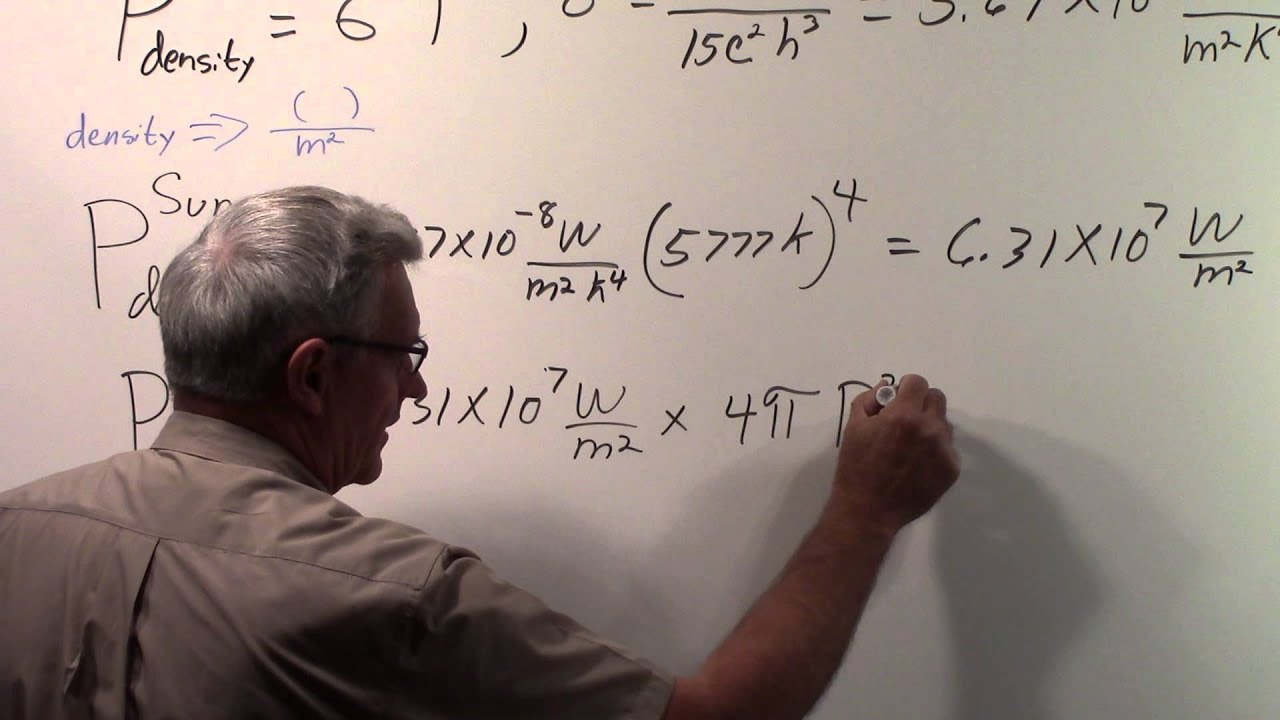The solar constant is the amount of power that the sun produces per unit area. It is measured in watts per square meter. The average solar constant is about 1,367 watts per square meter.
The solar constant varies depending on the time of day and the time of year. It also varies depending on the sun’s position in the sky. The solar constant is highest when the sun is directly overhead.
The solar constant is the amount of power that the sun delivers to a unit area at a distance of one astronomical unit (AU). It is commonly expressed in units of watts per square meter (W/m2). The value of the solar constant is approximately 1,368 W/m2.
The solar constant is important in calculating the amount of power that is available for solar panels and other solar energy applications. The higher the solar constant, the more power that is available.
The solar constant can be calculated using the following formula:
P = I * r2
Where:
P = Solar constant (W/m2)
I = Solar irradiance (W/m2)
r = Distance from the sun (AU)
The solar irradiance, I, is the amount of power that the sun delivers to a unit area.
It is typically measured in units of watts per square meter (W/m2).
The distance from the sun, r, is typically measured in units of astronomical units (AU). One AU is the distance from the sun to the Earth.
The solar constant is a important parameter in solar energy applications. It is used to calculate the amount of power that is available for solar panels and other solar energy devices.
Solar Constant and Solar Intensity on Earth
What is Solar Constant Si Unit?
The solar constant is the amount of power that the Sun emits per unit area. It is measured in watts per square meter (W/m2). The value of the solar constant is about 1,368 W/m2.
This means that if you were to take a square meter of the Sun’s surface, it would emit 1,368 watts of power. The solar constant is not really constant, however. It varies by about 6.3% over the course of a year.
This is due to the changing distance between the Sun and the Earth.
What is Solar Constant 11Th?
The solar constant is the amount of power that the sun produces per unit area. It is a measure of the sun’s intensity and is used to calculate the amount of power that solar panels can generate. The solar constant is typically measured in watts per square meter (W/m2).
The average solar constant is about 1,368 W/m2, but it can vary by about 6.3% during the year. The amount of power that solar panels can generate also varies depending on their efficiency. For example, a solar panel with an efficiency of 10% can generate 136 W/m2 of power.
Solar panels are most efficient when they are perpendicular to the sun’s rays. This means that the solar constant is highest at the equator and lowest at the poles.
The solar constant is a important factor to consider when designing solar power systems.
It is used to calculate the amount of power that solar panels can generate and the optimum orientation for solar panels.
What is the Value W M of the Solar Constant?
The solar constant is the amount of power that the sun emits per unit area. It is often denoted by the symbol “W/m^2” and is equal to about 1366 Watts per square meter. The solar constant is a very important value in many fields of science, including astronomy, climate science, and energy production.
The solar constant is not actually a constant value. It varies slightly over time, due to changes in the sun’s activity. The long-term average value of the solar constant is about 1366 Watts per square meter.
However, the value can vary by up to about 0.3% over the course of a year.
There are a number of factors that can affect the solar constant. One is the sun’s distance from Earth.
When the sun is closer to Earth, the solar constant is higher. Another is the sun’s “quiet” or “active” periods. During the sun’s active periods, there are more sunspots on the surface of the sun.
These sunspots emit more radiation, and so the solar constant is higher during these times.
The solar constant is a very important value in many fields of science. In astronomy, it is used to calculate the amount of power that a star emits.
In climate science, it is used to understand the Earth’s energy budget. And in energy production, it is used to calculate the amount of power that can be generated from solar panels.
What is Solar Constant And What is Its Value?
The solar constant is the amount of power that the sun produces per unit area. Its value is about 1366 watts per square meter. This means that if you were to take a square meter of the sun’s surface, it would produce about 1366 watts of power.
The solar constant is a measure of the sun’s power output, and its value is relatively constant.

Credit: digital.aakash.ac.in
Solar Constant Formula Dimensional
Solar Constant Formula Dimensional
In order to find the solar constant, we need to first understand what it is. The solar constant is the amount of power that the sun outputs per unit area that is perpendicular to the sun’s rays.
This power is in the form of electromagnetic radiation and is measured in watts per square meter (W/m^2).
Now that we know what the solar constant is, we can go about finding it. The most direct way to find the solar constant is to actually measure it.
This can be done by launching a satellite into space that is equipped with sensors that can measure the sun’s power output.
However, there is another way to find the solar constant and that is by using the Stefan-Boltzmann law. This law states that the power output of a black body is proportional to the fourth power of its temperature.
Since the sun is very close to being a black body, we can use this law to find its power output.
All we need to do is measure the sun’s temperature and then use the Stefan-Boltzmann law to find the solar constant. The sun’s temperature can be measured using spectroscopy and is found to be around 5800K.
Plugging this value into the Stefan-Boltzmann law, we find that the solar constant is approximately 1367 W/m^2.
This value is just an approximation since the sun is not a perfect black body. However, it is accurate to within a few percent and is the value that is most commonly used.
Solar Constant Calculator
Assuming you would like a blog post discussing a solar constant calculator:
A solar constant calculator is a tool that allows you to estimate the amount of solar radiation that hits a given area on Earth. This information is important for a variety of reasons, including determining the amount of solar energy that can be harnessed for solar power.
There are a few different ways to calculate the solar constant, but the most common is to use the latitude of the location in question. The solar constant is highest at the equator, and decreases as you move towards the poles. This is because the Earth’s atmosphere deflects some of the sunlight as it hits the planet, and the amount of deflection depends on the angle at which the light hits the atmosphere.
You can use a solar constant calculator to estimate the amount of solar radiation that hits a given area on Earth. This information is important for a variety of reasons, including determining the amount of solar energy that can be harnessed for solar power.
There are a few different ways to calculate the solar constant, but the most common is to use the latitude of the location in question.
The solar constant is highest at the equator, and decreases as you move towards the poles. This is because the Earth’s atmosphere deflects some of the sunlight as it hits the planet, and the amount of deflection depends on the angle at which the light hits the atmosphere.
You can use a solar constant calculator to estimate the amount of solar radiation that hits a given area on Earth.
This information is important for a variety of reasons, including determining the amount of solar energy that can be harnessed for solar power.
There are a few different ways to calculate the solar constant, but the most common is to use the latitude of the location in question. The solar constant is highest at the equator, and decreases as you move towards the poles.
This is because the Earth’s atmosphere deflects some of the sunlight as it hits the planet, and the amount of deflection depends on the angle at which the light hits the atmosphere.
You can use a solar constant calculator to estimate the amount of solar radiation that hits a given area on Earth. This information is important for a variety of reasons, including determining the amount of solar energy that can be harnessed for solar power.
Solar Constant of Earth
The solar constant is the average amount of solar radiation that Earth receives from the Sun. It is measured in watts per square meter (W/m2) and is a measure of the power of the Sun. The solar constant is important because it determines the amount of energy that Earth receives from the Sun.
The solar constant is not constant, but varies over time. The solar constant is highest in the summer and lowest in the winter. The solar constant also varies from day to day and from year to year.
The average solar constant over the past 30 years has been 1361 W/m2. The solar constant is highest at the equator and lowest at the poles. The solar constant is highest in the summer and lowest in the winter.
The solar constant also varies from day to day and from year to year. The average solar constant over the past 30 years has been 1361 W/m2.
Conclusion
The Solar Constant Formula is a mathematical formula used to calculate the amount of solar radiation received by a given area on Earth. The formula takes into account the angle of the sun, the distance between the sun and the Earth, and the Earth’s surface area. The Solar Constant Formula is used by scientists to study the Earth’s climate and to predict the amount of solar radiation that will be received by a given location on the Earth’s surface.