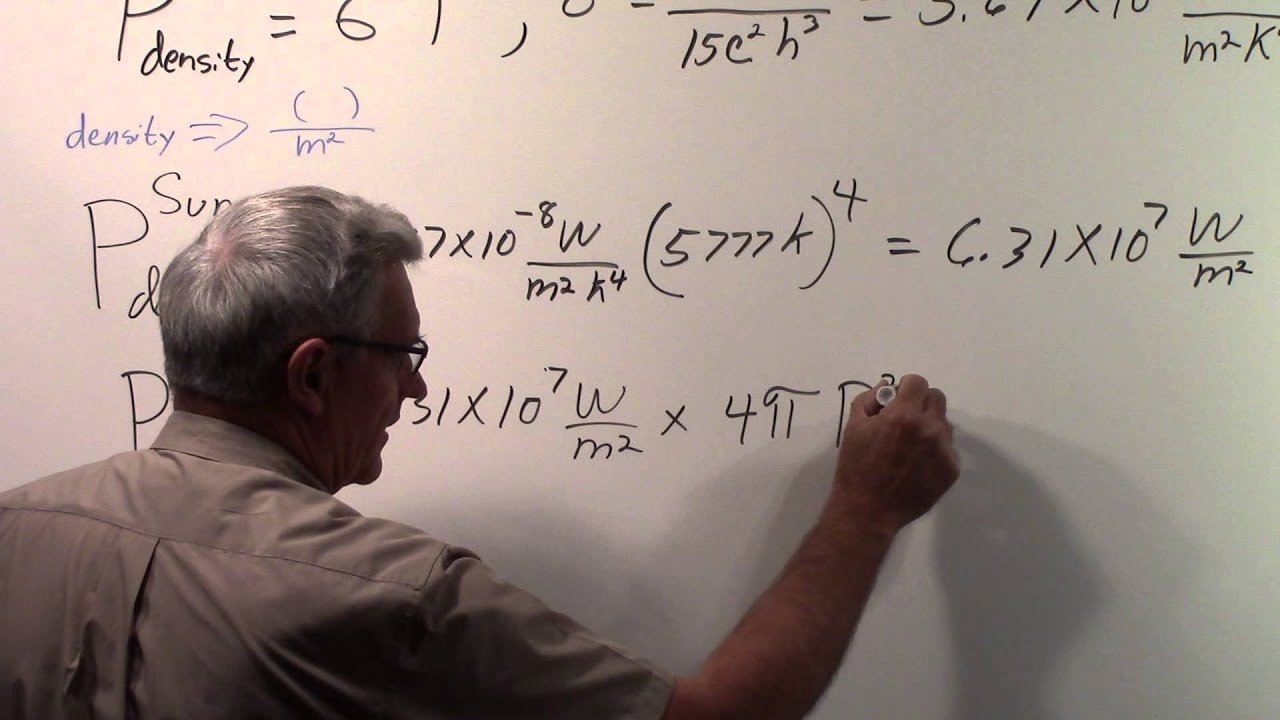The solar constant is a measure of the Earth-Sun distance. The average distance from the Sun to the Earth is about 93.3 million miles (150 million kilometers). The solar constant is the amount of power that the Sun emits at that distance.
The solar constant is about 1367 watts per square meter. That means that, on average, the Sun emits about 1367 watts of power for every square meter of the Earth’s surface.
The solar constant is a measure of the average amount of solar radiation that hits the Earth’s atmosphere. It’s been measured at about 1,368 watts per square meter. That means that, on average, the sun’s energy is hitting the Earth’s atmosphere with the force of 1,368 watts of electricity.
Solar Constant and Solar Intensity on Earth
What is the Solar Constant Quizlet?
The solar constant is the amount of radiation that the sun emits per unit of area. It is typically expressed in units of watts per square meter. The solar constant is a measure of the average amount of radiation that the sun emits over the course of a day.
The value of the solar constant is not constant over time, but it is generally considered to be about 1366 watts per square meter.
Where is the Solar Constant Measured?
The solar constant is the amount of power that the Sun delivers to a given point in space per unit of time. It is commonly measured in watts per square meter (W/m2). The solar constant includes all types of electromagnetic radiation emitted by the Sun, not just visible light.
The solar constant is not actually constant, but its value fluctuates over time. The main factor that affects the solar constant is the amount of sunspot activity on the Sun’s surface. Sunspots are dark, cooler areas on the Sun’s surface that are caused by intense magnetic activity.
When there are more sunspots, the Sun’s output of electromagnetic radiation decreases.
The solar constant is measured by a variety of instruments, including satellites, balloons, and ground-based telescopes. One of the most well-known measurements of the solar constant was taken by the Apollo astronauts as they traveled to the Moon.
They found that the solar constant was about 1366 W/m2.
The solar constant is an important quantity in the study of climate change. It is used to calculate the amount of power that is delivered to the Earth’s atmosphere and surface.
This power is then used to drive the Earth’s climate system.
Where is the Solar Constant Measured at Quizlet?
The solar constant is the amount of power that the Sun emits per unit area. It is measured at the top of the Earth’s atmosphere in a plane perpendicular to the Sun’s rays. The value of the solar constant is about 1366 watts per square meter.
What is Solar Constant Mcq?
The solar constant is the amount of power that the Sun delivers to a unit area at a distance of one astronomical unit (AU). It is commonly expressed in units of watts per square meter (W/m2). The solar constant includes all types of electromagnetic radiation from the Sun, not just the visible light that we see.
The solar constant is a measure of the average power delivered by the Sun over a unit area at a distance of one astronomical unit (AU). The solar constant is commonly expressed in units of watts per square meter (W/m2).
The value of the solar constant is not actually constant, but varies over time.
The variation is thought to be caused by changes in the Sun’s magnetic field. The solar constant is also affected by the Earth’s distance from the Sun, which varies as the Earth orbits the Sun. The Earth is closest to the Sun in January (perihelion), and farthest from the Sun in July (aphelion).
The solar constant is important for climate studies, because it determines the amount of power that is available for driving the Earth’s climate system. The solar constant also plays a role in the habitability of a planet, by determining the amount of power that is available for photosynthesis.

Credit: www.allthescience.org
The Solar Constant is a Measure of Quizlet
The solar constant is the amount of power that the sun produces per unit area. It is measured in watts per square meter. The average solar constant is about 1,368 watts per square meter.
The solar constant varies depending on the time of day, the time of year, and the location on Earth.
What is the Value of Solar Constant in W/M2
The solar constant is the amount of power that the sun produces per unit area. It is typically expressed in watts per square meter (W/m2). The value of the solar constant is important for many applications, including solar energy production, solar radiation protection, and climate modeling.
The solar constant is not a constant value, but rather it varies over time. The variations are caused by a number of factors, including changes in the sun’s output, the Earth’s orbit, and atmospheric conditions. The value of the solar constant also varies across the globe, due to the Earth’s rotation and the tilt of its axis.
Despite its name, the solar constant is not a constant value. However, its average value over the course of a year is 1,368 W/m2. This value is important for many applications, including solar energy production and climate modeling.
Solar Constant Formula
The solar constant is the amount of power that the sun emits per unit area. It’s usually expressed in watts per square meter. The value of the solar constant varies depending on the wavelength of the light.
For example, the solar constant for visible light is about 1,368 watts per square meter.
The solar constant is important because it determines the amount of power that solar panels can generate. The higher the solar constant, the more power the panels can generate.
The solar constant also affects the amount of power that solar cells can generate. The higher the solar constant, the more power the cells can generate.
The solar constant can be calculated using the following formula:
Solar constant (in watts per square meter) = 1,368 x (wavelength in nanometers)
For example, if you want to calculate the solar constant for visible light, you would use the following formula:
Solar constant (in watts per square meter) = 1,368 x (wavelength in nanometers)
Solar constant (in watts per square meter) = 1,368 x (650 nanometers)
Conclusion
. . The Solar Constant is a Measure of the Amount of Energy Coming From the Sun. It’s Not Actually Constant, Though.