Monday, August 21, 2017, all of North America will be treated to an eclipse of the sun. Anyone within the path of totality can see one of nature’s most awe inspiring sights – a total eclipse of the sun. This path, where the moon will completely cover the sun and the sun’s tenuous atmosphere – the corona – can be seen, will stretch from Salem, Oregon to Charleston, South Carolina.
Observers outside this path will still see a partial solar eclipse where the moon covers part of the sun’s disk.
A solar eclipse occurs when the moon passes between the sun and the earth, blocking out the sun’s light. A 90% solar eclipse is when 90% of the sun’s light is blocked out. This can happen when the moon is at a certain point in its orbit around the earth.
What does a 90% solar eclipse look like?
If you’re in the path of totality, a 90% solar eclipse will look like a partial eclipse. The sun will be partially covered by the moon, and the sky will darken.
You may be able to see some of the sun’s corona, or outer atmosphere.
If you’re not in the path of totality, you’ll see a 90% solar eclipse as a partial eclipse. The sun will be partially covered by the moon, and the sky will darken.
A 90% solar eclipse is a rare event. The last one occurred on August 21, 2017. The next one won’t occur until 2045.
If you want to see a 90% solar eclipse, make sure you have the proper safety gear. Never look directly at the sun, even during an eclipse. Solar eclipse glasses or a solar viewer can help you safely view the eclipse.
Total Solar Eclipse (2017)
What Does a Full Solar Eclipse Look Like?
When the moon moves in front of the sun during a solar eclipse, it blocks out most of the sun’s light. This leaves only the sun’s outer atmosphere, or corona, visible. The corona is usually too faint to see because it is so much dimmer than the sun’s bright disk.
But during a total eclipse, the corona is clearly visible and is often described as looking like a halo or crown around the sun.
The corona can be seen in different ways during a total eclipse, depending on the sun’s activity at the time. Sometimes the corona is bright and extends far out from the sun.
Other times it is faint and only extends a short distance from the sun.
People who have seen a total eclipse often say that it is a life-changing experience. The sight of the sun’s corona is so beautiful and so different from anything that can be seen normally, that it is hard to describe in words.
If you want to see a total eclipse, you will need to be in the path of totality. This is the shadow cast by the moon as it moves across the earth. The path of totality is usually about 60 to 70 miles wide, and the moon’s shadow moves across the earth at about 1,000 miles per hour.
There are usually two total eclipses each year, although sometimes there are three. total eclipses are not evenly spaced throughout the year, because the earth’s orbit around the sun is elliptical, not circular. This means that the earth is closer to the sun at some times of the year than at others.
When the earth is closer to the sun, the moon’s shadow moves faster across the earth, so there is less time to see the total eclipse.
The best place to see a total eclipse is often not in the path of totality. This is because the weather is often better away from the path of totality, and because the sun’s corona is often more visible when the moon is not directly in front of the sun.
If you want to see a total eclipse, you should make sure that you are in a place where the weather is good and that you have a clear view of the sun.
What Does a Maximum Eclipse Look Like?
When the Moon completely covers the Sun during an eclipse, it looks like a black disk has taken a bite out of the Sun. This is what’s called a total eclipse.
The Sun’s outer atmosphere, the corona, is much fainter than the Sun’s bright disk.
During a total eclipse, the corona becomes visible to the naked eye because the bright disk of the Sun is completely blocked by the Moon.
The corona looks like a white halo around the black disk of the Moon. It’s actually made up of streamers of hot plasma that flow outward from the Sun’s surface.
The corona is usually only visible during a total eclipse, but it can also be seen during a partial eclipse, when the Moon covers only part of the Sun.
What is the Rarest Eclipse on Earth?
There are four types of eclipses that can occur on Earth: total, annular, partial, and umbral. Of these, the rarest is the total eclipse.
A total eclipse occurs when the sun, moon, and Earth are perfectly aligned, and the moon’s shadow falls on the Earth’s surface.
This alignment is a rare occurrence, because the moon’s orbit is tilted relative to the Earth’s orbit around the sun. As a result, total eclipses are only visible from specific locations on Earth.
The next total eclipse will occur on July 2, 2019 and will be visible from parts of South America.
After that, the next total eclipse will occur on December 14, 2020 and will be visible from parts of Africa and Asia.
Total eclipses are often considered to be the most spectacular type of eclipse, because they offer a rare opportunity to see the sun’s atmosphere – the corona. The corona is normally only visible during a total eclipse, when the bright light of the sun is blocked by the moon.
What is the Rarest Type of Solar Eclipse?
A total solar eclipse is one of the most amazing astronomical events that one can witness. It is also one of the rarest types of solar eclipse.
A total solar eclipse occurs when the moon completely covers the sun, resulting in the sun’s disk appearing to vanish.
This can only happen when the sun, moon and Earth are perfectly aligned. The moon’s orbit around Earth is tilted so that, usually, the moon’s shadow misses our planet. But about twice each year, the three bodies line up just right so that the moon’s shadow falls on Earth.
If the alignment is perfect, the moon’s shadow will travel across the entire surface of our planet, from one coast to the other. This is known as a total solar eclipse. But if the alignment is off by even a little bit, the moon’s shadow will miss Earth entirely, resulting in an annular solar eclipse.
Total solar eclipses are quite rare. In any given location on Earth, a total eclipse happens only once every 375 years on average. But because the Earth is so big, total eclipses are actually not that rare.
Each year, there are usually two total eclipses somewhere on the planet.
The last total solar eclipse visible from the contiguous United States occurred on August 21, 2017. The next one will occur on April 8, 2024.
So, to sum it up, the rarest type of solar eclipse is the total solar eclipse.
Credit: eclipse.aas.org
When is the Next Solar Eclipse
A solar eclipse occurs when the moon passes between the sun and the earth, and the moon’s shadow falls on the earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the moon’s disk completely covers the sun’s disk. The last total solar eclipse occurred on August 21, 2017.
The next total solar eclipse will occur on July 2, 2019.
Types of Solar Eclipse
A solar eclipse occurs when the moon passes between the sun and the earth, blocking out the sun’s light. There are three types of solar eclipse: total, partial, and annular.
A total solar eclipse occurs when the moon’s shadow completely covers the sun.
This can only happen when the sun, moon, and earth are perfectly aligned. The moon’s shadow is cast on the earth, and anyone within the shadow’s path will see the sun completely blocked out.
A partial solar eclipse occurs when the moon’s shadow covers only part of the sun.
This can happen when the sun, moon, and earth are not perfectly aligned. The moon’s shadow is cast on the earth, and anyone within the shadow’s path will see the sun partially blocked out.
An annular solar eclipse occurs when the moon’s shadow does not reach the earth.
This can happen when the sun and moon are at different distances from the earth. The moon’s shadow is cast on the earth, but anyone within the shadow’s path will see the sun as a ring of light around the moon.
When Do Solar Eclipses Occur
A solar eclipse occurs when the moon passes between the sun and the Earth, and the moon casts a shadow on the Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the moon’s shadow completely covers the sun, and a partial solar eclipse occurs when the moon’s shadow covers part of the sun.
Solar eclipses can only occur during the new moon phase, when the moon is positioned between the sun and the Earth.
The moon’s orbit is inclined at about 5 degrees to the Earth’s orbit around the sun, so the moon usually passes above or below the sun as seen from the Earth. But about twice each year, the moon’s orbit intersects the Earth’s orbit and an eclipse can occur.
Total solar eclipses are rare events.
A total eclipse can only be seen from a small area on the Earth’s surface, and even then, only when the sun is high in the sky. The last total solar eclipse visible from the continental United States occurred on February 26, 1979. The next one will occur on August 21, 2017.
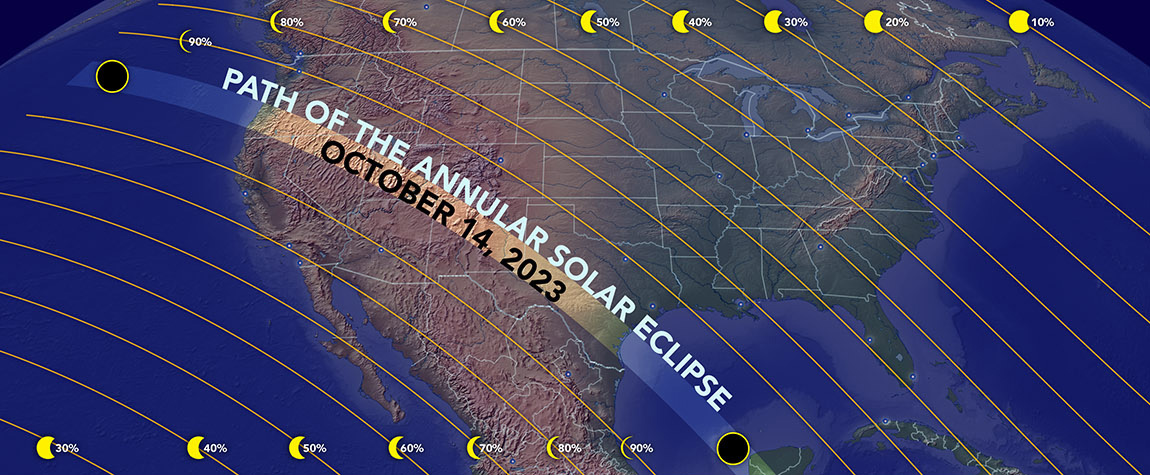
Partial solar eclipses are much more common than total eclipses. A partial eclipse can be seen from a larger area on the Earth’s surface, and they often occur when the sun is lower in the sky. The next partial solar eclipse visible from the continental United States will occur on October 14, 2023.
Conclusion
A solar eclipse occurs when the moon passes in front of the sun, blocking its light. A total solar eclipse occurs when the moon’s shadow completely covers the sun, and a partial solar eclipse occurs when the moon’s shadow covers only part of the sun.
On August 21, 2017, a total solar eclipse will be visible in a 70-mile-wide path spanning from Oregon to South Carolina.
Outside of this path, viewers in the continental United States will see a partial solar eclipse, with the moon blocking out anywhere from 60-80% of the sun.
So, what does a 90% solar eclipse look like? Essentially, it will look like a partial eclipse, but with the sun 10% visible.
The sky will darken, but not as much as it would during a total eclipse. And, because the moon is not completely blocking the sun, viewers will not see the sun’s corona – the outermost layer of its atmosphere.
So, if you’re not in the path of the total eclipse, don’t worry – you’ll still be able to see a spectacular show on August 21st!