The sun is a star that is located at the center of the solar system. It is the Earth’s only natural satellite. The sun is about 150,000 times the size of the Earth and has the mass of about 333,000 Earths.
The sun is a medium-sized star and is about halfway through its life. It will eventually become a red giant and then a white dwarf.
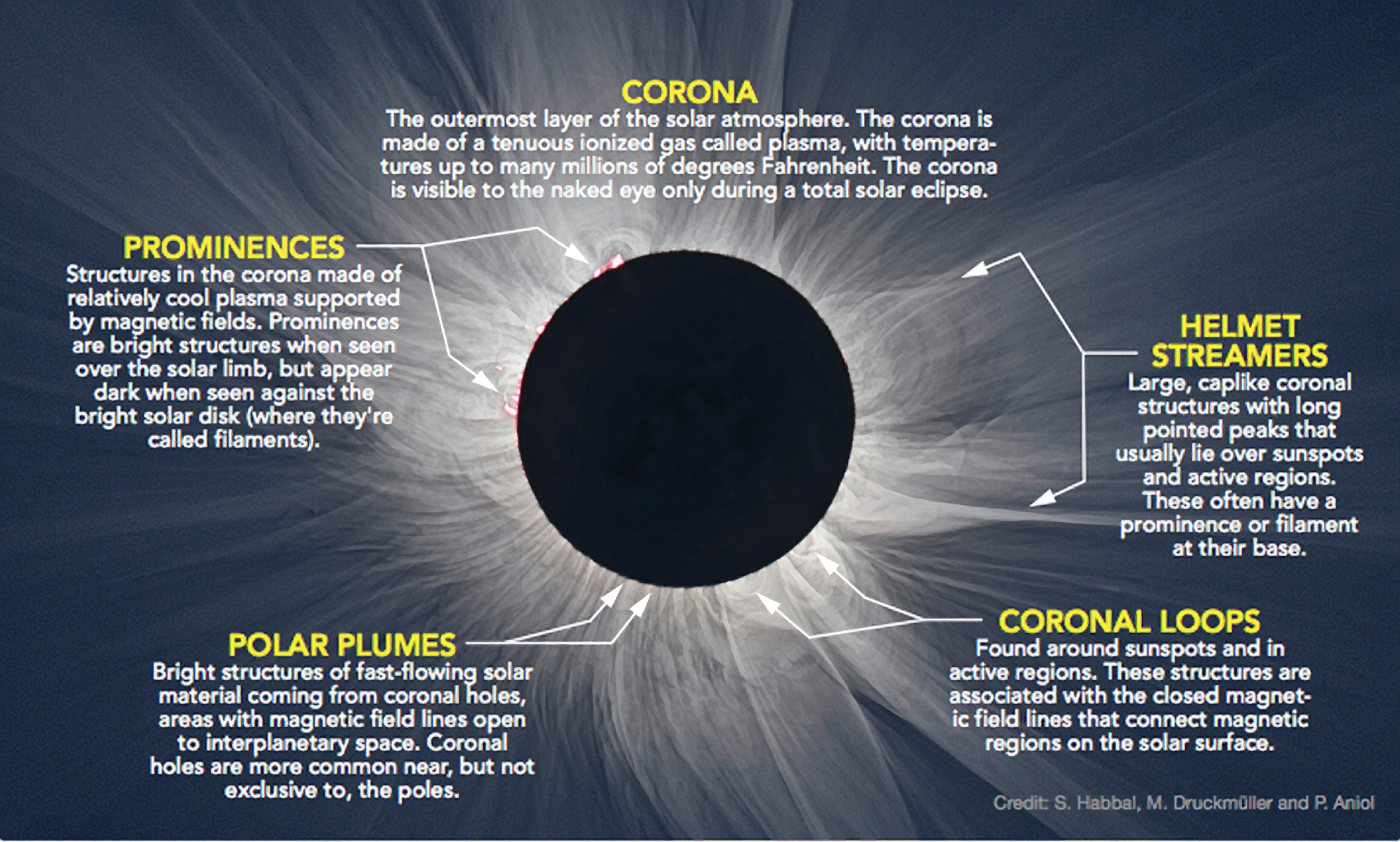
A total solar eclipse is an amazing event to witness. The sun’s outermost layer, the corona, is visible during a total solar eclipse. The corona is a faint, halo-like aura of plasma that surrounds the sun.
It is usually only visible during a total solar eclipse, when the moon blocks out the sun’s bright disk.
Credit: solar-center.stanford.edu
-What Causes a Total Solar Eclipse
A total solar eclipse occurs when the moon completely covers the sun’s disk, as seen from Earth. This can happen only at new moon, when the sun and moon are in conjunction as seen from Earth. If the alignment is perfect, the moon blocks all direct sunlight from reaching Earth and casts a shadow on the planet.
There are three types of solar eclipses—total, partial, and annular. A total eclipse is when the sun is completely blocked by the moon. A partial eclipse is when the sun is only partially blocked.
And an annular eclipse is when the sun is not completely covered by the moon, but the moon appears as a bright ring around the sun.
Total solar eclipses are rare because the moon’s orbit around Earth is tilted. Most of the time, the moon is above or below the sun’s disk as seen from Earth, so a total eclipse doesn’t happen.
But about twice a year, the moon’s orbit takes it in front of the sun. When this happens, we can see a total eclipse.
The next total eclipse of the sun will occur on July 2, 2019.
It will be visible in a narrow path across the southern Pacific Ocean, Chile, and Argentina.
Less Than Five – Layers of the Sun Explained – Outer Layers
A Circle of Light And Bright Spot During a Solar Eclipse is Called
A solar eclipse occurs when the moon passes between the sun and the earth, blocking out the sun’s light. The moon’s shadow cast onto the earth’s surface is called the umbra. The umbra is the darkest part of the shadow, and it is where the sun is completely blocked out.
The lightest part of the shadow is called the penumbra. In the penumbra, the sun is only partially blocked out.
During a solar eclipse, the moon’s shadow falls on the earth’s surface and creates a circle of light.
This circle is called the umbra. The umbra is the darkest part of the shadow, and it is where the sun is completely blocked out. The lightest part of the shadow is called the penumbra.
In the penumbra, the sun is only partially blocked out.
When the sun is completely blocked out by the umbra, it creates a bright spot in the center of the shadow. This bright spot is called the diamond ring effect.
The diamond ring effect is created by the sun’s light shining through the moon’s valleys.
The umbra and penumbra are both part of the moon’s shadow. The umbra is the darkest part of the shadow, and it is where the sun is completely blocked out.
The penumbra is the lightest part of the shadow, and it is where the sun is only partially blocked out.
Which Layer of the Sun is the Hottest?
Most people think that the sun’s core is the hottest layer, but they would be wrong. The sun’s photosphere is actually the hottest layer. The photosphere has a temperature of around 10,000 degrees Fahrenheit.
The sun’s core has a temperature of around 27 million degrees Fahrenheit.
Why are Sunspots Darker Than Surrounding Areas
The sun is basically a huge ball of gas that is constantly undergoing nuclear fusion. This fusion creates a lot of heat and light. The sun also has a magnetic field that extends out into space.
This magnetic field is constantly changing and this causes disruptions in the flow of plasma on the sun’s surface. These disruptions are called sunspots.
Sunspots are usually dark because the plasma in the sunspot is cooler than the plasma in the surrounding area.
The reason the plasma is cooler is because the sunspot is not receiving as much heat from the nuclear fusion that is going on inside the sun. The sunspot is also not receiving as much light because the plasma is not as hot and thus it does not emit as much light.
Sunspots can be very large, up to several thousand kilometers in diameter.
They are usually dark, but sometimes they can be very bright. Bright sunspots are usually associated with strong magnetic fields.
A Total Solar Eclipse Would Be Possible in Which Part of the Moon’S Shadow?
A total solar eclipse is when the sun and moon are in alignment, and the moon’s shadow falls on the earth. This can only happen during a new moon, when the sun and moon are on the same side of the earth. The moon’s shadow is actually divided into two parts: the umbra and the penumbra.
The umbra is the dark inner shadow, where the sun is completely blocked out. The penumbra is the outer shadow, where the sun is only partially blocked.
A total solar eclipse is only possible in the umbra, when the sun is completely blocked out.
However, a partial eclipse is possible in either the umbra or penumbra. So, if you’re in the right place at the right time, you could see a total solar eclipse!
Conclusion
A total solar eclipse occurs when the moon passes in front of the sun, blocking its light. The sun’s outer layer, the corona, is visible during a total eclipse. The corona is usually only visible during a total eclipse because it is so faint.
The corona is the sun’s atmosphere and is made up of plasma, a hot, ionized gas. The temperature of the corona can be up to 1 million degrees Celsius. The corona is not always visible during a total eclipse, however.
If the sun is active, such as during a solar flare, the corona may be obscured.
